An Inrush Current Limiter (ICL) is an effective tool to prevent electrical equipment from overheating caused by inrush current during switch-on. Inrush current refers to the maximum surge of incoming current from a power source, which can be as much as 2 to 3 times the steady-state current of the attached device. Inrush Current Calculators can help determine the appropriate resistance versus temperature curve to select the correct Inrush Current Limiter.
Switching power supplies, DC motors, and lighting ballasts can experience high peak inrush current at turn-on unless inrush current protection is implemented. Moreover, magnetic devices such as electric motors or transformers can draw as much as 30 times their steady-state current at switch-on.
In the absence of inrush current protection, the amount of inrush current drawn is only limited by the line impedance and the equivalent series resistance of a capacitor. Despite the fact that modern circuit systems operate more efficiently and maintain lower impedance, inrush current remains a significant issue.
The overall efficiency of low impedance can also contribute to high inrush current, increasing the risk of equipment overheating during start-up. Implementing inrush current limiters can help prevent equipment from overheating due to inrush current. Ametherm provides a wide range of inrush current limiters that can be viewed on their website, along with information on how to reduce inrush current.
How do I Select the Right Inrush Current Limiter for My Application?
Inrush current limiters are designed with different characteristics like resistance versus temperature curve to accommodate numerous applications. Because of this, it is necessary to make some calculations based on your system requirements to select the best inrush current limiter for your needs.
At a minimum, you will need to know:
- Maximum Output Power: Based on specific system or design requirements, this is a variable and is relevant to the steady state current of the application
- Input Voltage: This is the available incoming line voltage to the application in question. For example, 110 or 120 VAC
You should also be aware of the following information:
- Reset Time: How often the system will be switched on/off during a given time frame
- Single Phase or Three Phase: Incoming voltage pulled in from either a single line or three lines
- Filter or Link Capacitor Value: Value in Micro Farads. Quantifies the magnitude of capacitance
- Scope Trace of Inrush Current: A snapshot of inrush current at a moment in time
- Fuse or Circuit Breaker Rating if applicable
- Inrush Current Rating of Diode Bridge if applicable
Example Problem Statement
Current Situation: A 1500-watt switch mode power supply trips a 20-amp breaker at turn-on due to high inrush current. How do you stop the breaker from tripping?
Given Information:
- 230 VAC input voltage
- Peak Voltage = 230 VAC * 1.414 = 325.22 V
- Filter capacitance of 2700μF
- 90% Efficiency
Solution: You should add an Inrush Current Limiter to reduce high inrush current at turn-on which should stop the breaker from tripping due to the high inrush current.
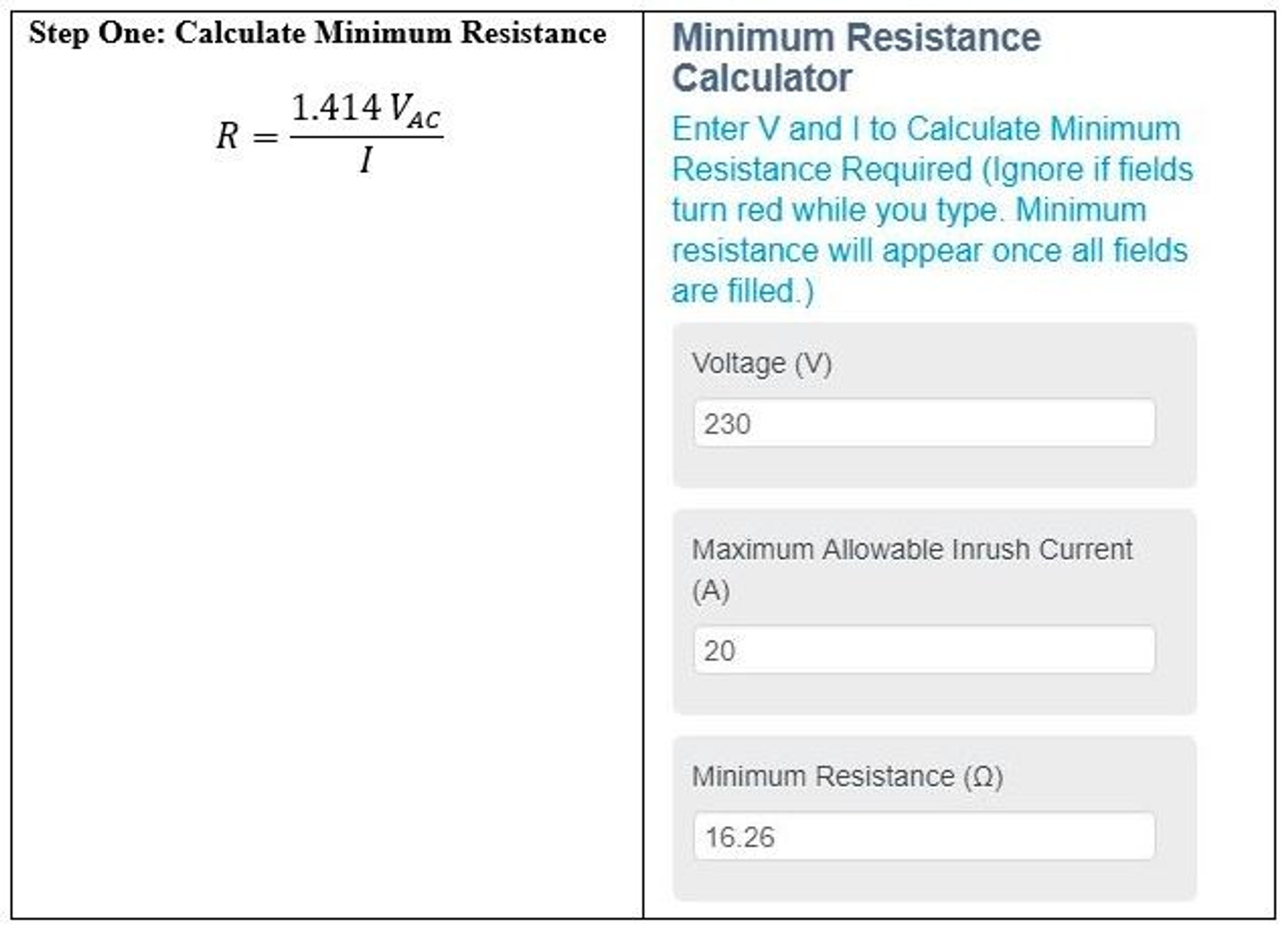
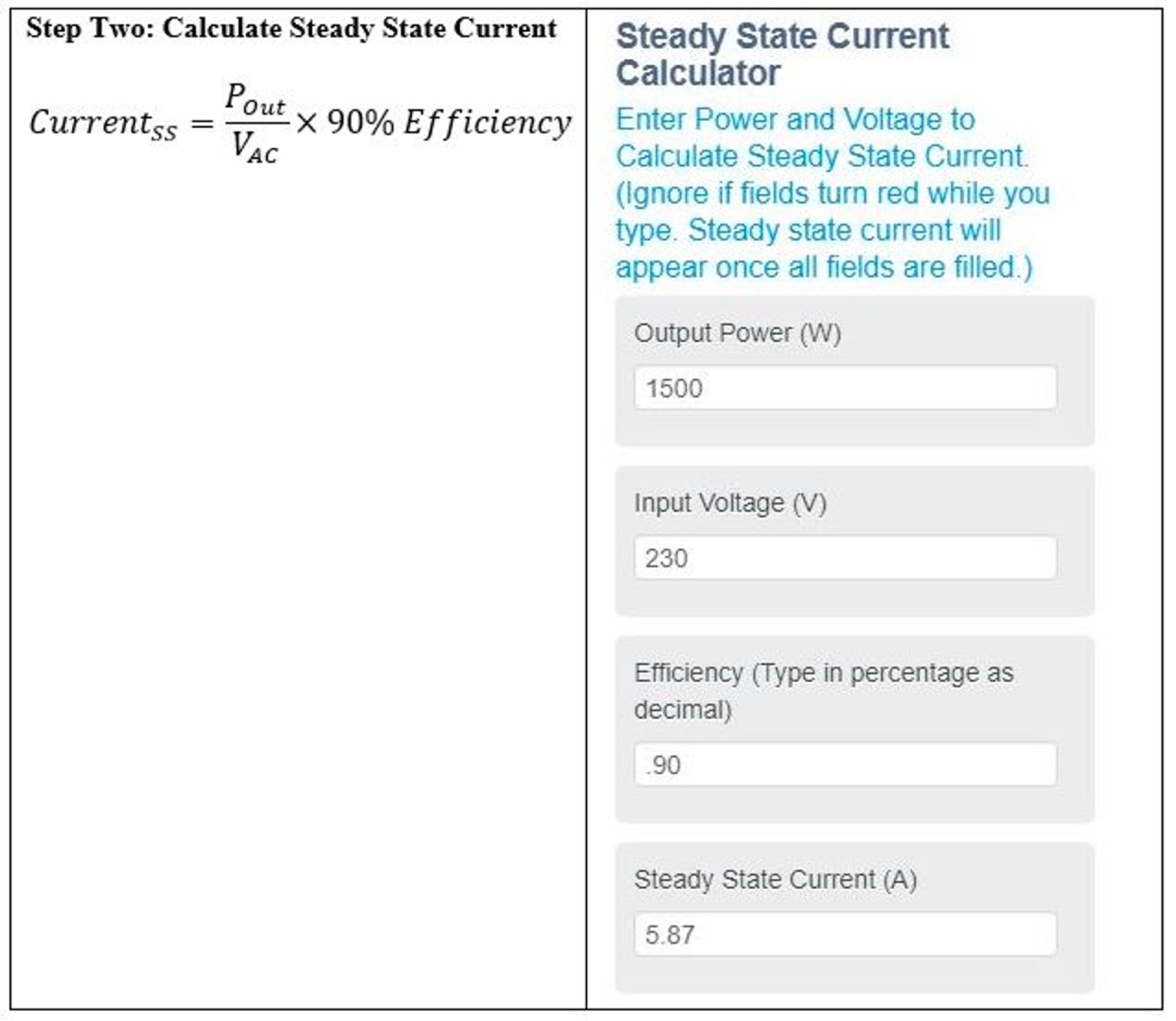
The above calculations recommend Inrush Current Limiter MS32 20008
- 20 ohms
- 250J
- 8 amp-continuous
Why We Are One
For over 40 years, IBS Electronics Group has provided a broad range of integrated supply chain and electronicsmanufacturing solutions tailored specific to our customer's operations. As your one source for the industry’s top brands all in one place, our engineers specialize in reducing supply chain complexity and are here to provide you with dedicated support from prototype to production.




.png)


.png?resizemode=force&maxsidesize=96)